Supported color formats¶
RGB¶
The RGB color model uses 3 colors: Red, Green, and Blue to construct all the colors. Each parameter in this format represents the intensity of the colors, expressed on a scale dependent on its bit depth.
Name |
VL42 Identifier |
|---|---|
RGB332 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB332 |
ARGB444 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_ARGB444 |
RGBA444 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGBA444 |
ABGR444 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_ABGR444 |
BGRA444 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_BGRA444 |
ARGB555 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_ARGB555 |
RGBA555 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGBA555 |
ABGR555 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_ABGR555 |
BGRA555 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_BGRA555 |
RGB565 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB565 |
BGR24 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_BGR24 |
RGB24 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGB24 |
ABGR32 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_ABGR32 |
BGRA32 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_BGRA32 |
RGBA32 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_RGBA32 |
ARGB32 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_ARGB32 |
YUV¶
The YUV color model consists of 3 elements:
Y is the brightness or luminescence information
U is the red color (chroma) difference value
V is the blue color (chroma) difference value
Both color difference values can be calculated by subtracting the Y value from the RGB color space’s blue component (for U) or red component (for V). Raviewer uses the following formulas to calculate each of the YUV values:
Y = R * .299000 + G * .587000 + B * .114000
U = R * -.168736 + G * -.331264 + B * .500000 + 128
V = R * .500000 + G * -.418688 + B * -.081312 + 128
Name |
VL42 Identifier |
Pixel plane |
|---|---|---|
UYVY |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_UYVY |
PACKED |
YUYV |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV |
PACKED |
VYUY |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_VYUY |
PACKED |
YVYU |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_YVYU |
PACKED |
NV12 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_NV12 |
SEMI-PLANAR |
NV21 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_NV21 |
SEMI-PLANAR |
I420 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUV420 |
PLANAR |
YV12 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_YVU420 |
PLANAR |
I422 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUV422P |
PLANAR |
Bayer RGB¶
Bayer format is a raw video format produced by image sensors that include a Bayer filter. A Bayer filter is a color filter array in which RGB color filters are arranged on a grid of square photosensors. A Bayer filter uses two green filter elements for each red and blue filter element. The filter array can be arranged in 4 distinct patterns. Their names are derived from the order of the filters in a single 2x2 pixel square:
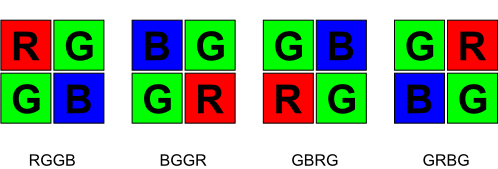
Bayer format is a popular raw image format used in many modern color image sensors.
Name |
VL42 Identifier |
|---|---|
RGGB |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_SRGGB8 |
RG10 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_SRGGB10 |
RG12 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_SRGGB12 |
RG16 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_SRGGB16 |
Grayscale¶
In the grayscale color format, each pixel only conveys intensity information. This information can be expressed on a scale dependent on its bit depth, where the minimum value represents white, and the maximum value represents black.
Name |
VL42 Identifier |
|---|---|
GRAY |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_GRAY |
GRAY10 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_Y10 |
GRAY12 |
V4L2_PIX_FMT_Y12 |
Adding new color formats¶
Currently, two classes can be used to describe color formats: ColorFormat and SubsampledColorFormat (found in app/image/color_format.py).
To create a new color format:
In
color_format.py, add a new instance of one of the color format classes with the appropriate fields filled in under the AVAILABLE_FORMATS list.Add parsing and displaying functions to the
AbstractParserincommon.py.You can also use other parsers from the folder or implement a new one.The utility provides a proper parser by checking color format parameters (mainly
PixelFormat) so make sure that your new color format has a valid translation of parameters to one of the parsers (you can find this functionality inapp/parser/factory.py).
Note
Keep in mind that if you choose to implement a new parser, remember that parse() should return a one-dimensional ndarray with values read from the binary file, while display() should return an RGB-formatted 3-dimensional ndarray consisting of original color format values converted to RGB24.