Optimizing and comparing instance segmentation models¶
This example demonstrates how to optimize computer vision models and compare different optimizers.
Base model used for demonstration is going to be YOLACT, short for “You Only Look At CoefficientTs” which is a fully convolutional model for real-time instance segmentation.
We will also need dataset for evaluation purposes - in this case it is going to be OpenImagesDatasetV6.
Model will be deployed on CPU and GPU using following Kenning compilers:
ONNXCompiler - wrapper for optimizing and converting models to format compliant for ONNX Runtime.
TVMCompiler - wrapper for TVM deep neural network compiler.
Setup¶
To install all necessary dependencies run:
pip install "kenning[object_detection,tvm,onnxruntime,reports] @ git+https://github.com/antmicro/kenning.git"
Experiments on CPU¶
TVM optimization¶
The scenario for TVM compilation may look as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | |
In this scenario:
model_pathpoints to a location of the YOLACT model in ONNX format. It can be either local file or a remote URL.kenning://is a special schema for Kenning’s demonstration models.datasettells to use Open Images dataset. The model will be downloaded to./build/OpenImagesDatasetV6. Thetaskfield allows to specify whether the dataset is used for instance segmentation or object detection.optimizerscontains only one element -TVMCompiler. In there we specify input model framework (onnx), and tell to usellvmtarget withopt_levelequal to 3 (applying all possible optimizations not directly affecting model’s output).runtimetells Kenning to useTVMRuntimefor model execution, on CPU target.
To optimize and test the defined scenario, run:
python -m kenning optimize test \
--cfg yolact-tvm-cpu-detection.yml \
--measurements ./build/yolact-tvm.json \
--verbosity INFO
ONNX Runtime execution of model¶
Switching to a different runtime is a matter of changing several lines in the scenario as shown below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | |
ONNXRuntime in this specific scenario acts as a passthrough for an existing ONNX model.
The main change in runtime lies in ONNXRuntime, where execution_providers holds a list of possible layer executors starting from the most preferred one.
For CPU-only execution CPUExecutionProvider is required.
This scenario can be executed with:
python -m kenning optimize test \
--cfg yolact-onnx-cpu-detection.yml \
--measurements ./build/yolact-onnx.json \
--verbosity INFO
Comparison¶
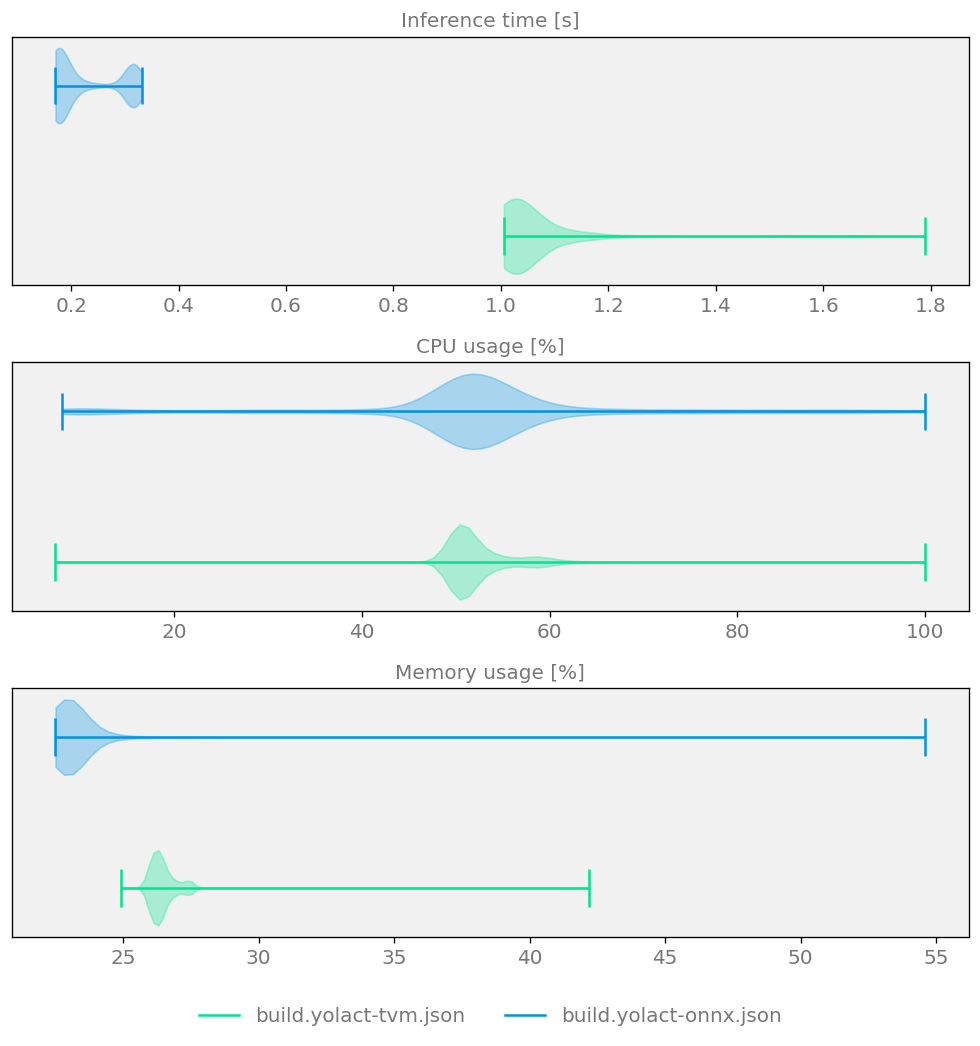
Figure 6 Sample comparison plot demonstrating model size, speed and quality for two YOLACT Optimizers¶
To create a comparison report comparing performance and model quality for the above optimizers, run:
python -m kenning report \
--report-path build/yolact-report/report.md \
--report-name "YOLACT detection report" \
--root-dir build/yolact-report \
--img-dir build/yolact-report/imgs \
--report-types performance detection \
--measurements build/yolact-tvm.json build/yolact-onnx.json
GPU Experiments¶
Info
This example requires a CUDA-enabled GPU for proper execution, along with following dependencies:
CUDA (11.8 is recommended version)
CUDNN (8 is recommended version)
NVCC
NVRTC
CUDA Toolkit
NVML (for report generation)
TVM optimization¶
Open for instructions on building TVM with CUDA enabled
To run TVM on GPU you need to build it with necessary libraries included - follow Building from source in TVM documentation.
On Linux-based distributions:
Uninstall previously installed TVM version (supports only CPU):
pip uninstall -y apache-tvmEnsure installation of:
GCC >= 7.1 / Clang >= 5.0
CMAKE >= 3.24
LLVM >= 15
Git
Python >= 3.8
Clone tvm repository:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/apache/tvm -b v0.14.0 tvmConfigure the build by setting the necessary flags in
config.cmake:cd tvm && mkdir build && cd build cp ../cmake/config.cmake . echo "set(USE_CUBLAS ON)">> config.cmake echo "set(USE_CUDA ON)" >> config.cmake echo "set(USE_CUDNN ON)" >> config.cmake echo "set(USE_MICRO ON)" >> config.cmake echo "set(USE_LLVM ON)" >> config.cmakeBuild TVM with the following command:
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/ .. && make -j $(nproc) && make install && ldconfig cd ../..Add built libraries to
TVM_LIBRARY_PATH:export TVM_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/lib/Install new TVM version using
pip:pip install ./tvm/python
CUDA runtime is very strict about gcc versions so if you get an error unsupported GNU version! gcc versions later than 11 are not supported!, then set the necessary flag:
export NVCC_APPEND_FLAGS='-allow-unsupported-compiler'
To run TVM optimization of YOLACT for GPU, the previous TVM scenario requires changes in:
TVMCompiler- need to settargettocuda -libs=cudnn,cublasTVMRuntime- need to configuretarget_device_contexttocuda
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | |
To run it:
python -m kenning optimize test \
--cfg yolact-tvm-gpu-detection.yml \
--measurements ./build/yolact-gpu-tvm.json \
--verbosity INFO
ONNX optimization¶
Open for instructions on installing ONNX Runtime with CUDA enabled
If you want to run ONNX on GPU you need to install onnxruntime-gpu:
Uninstall CPU-only variant with:
pip uninstall -y onnxruntimeInstall GPU-enabled ONNX Runtime:
pip install "kenning[onnxruntime_gpu] @ git+https://github.com/antmicro/kenning.git"Add necessary CUDA libraries to path:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/cuda/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH export PATH=/usr/local/cuda/bin:$PATH
The only difference compared to CPU-only execution using ONNX Runtime lies in adding new executor in the runtime:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |
Run the scenario as follows:
python -m kenning optimize test \
--cfg yolact-onnx-gpu-detection.yml \
--measurements ./build/yolact-gpu-onnx.json \
--verbosity INFO
Comparison of GPU runtimes¶
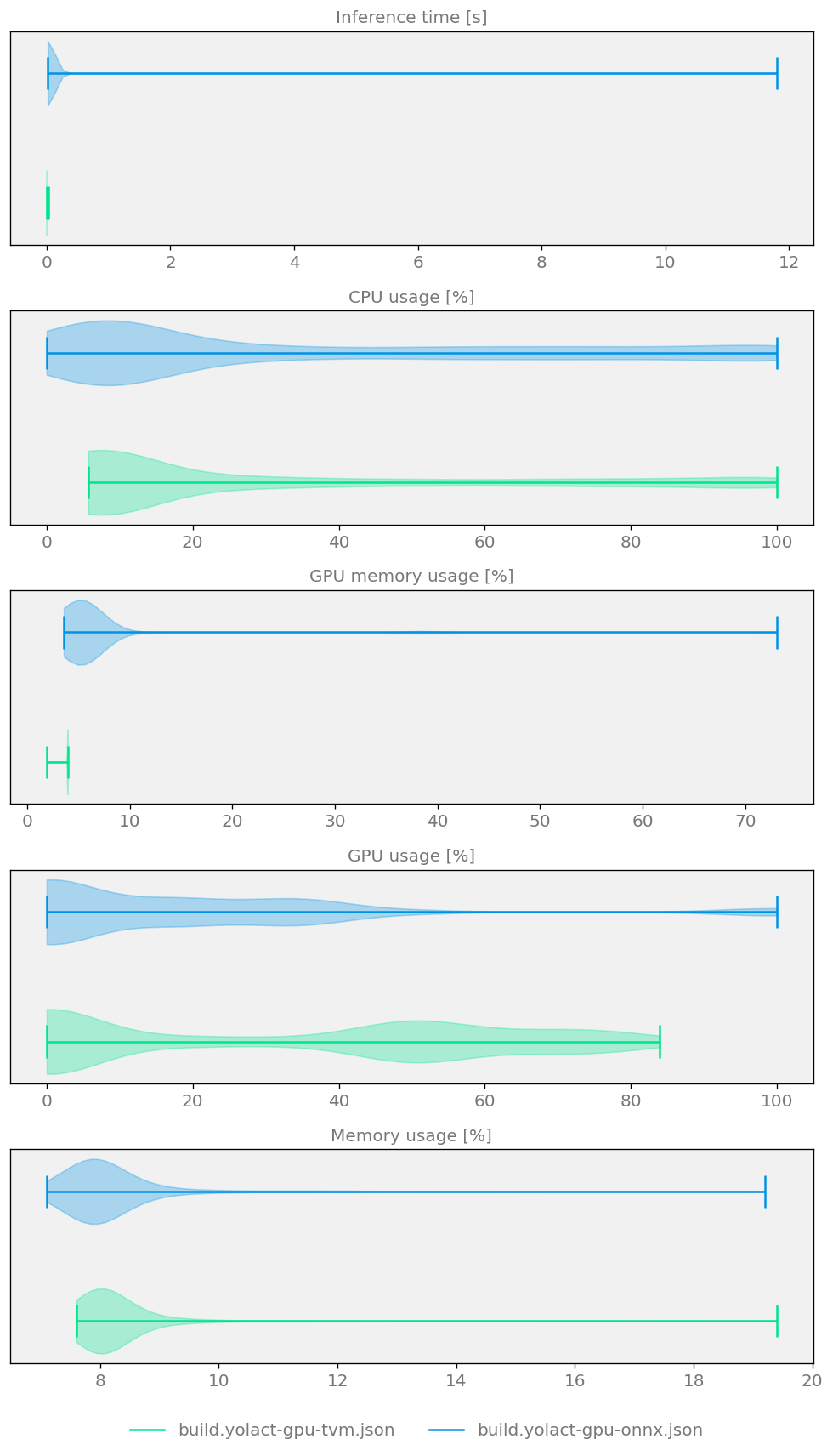
Figure 7 Model size, speed and quality comparison for two YOLACT Optimizers running on CUDA GPU¶
To create a comparison report comparing performance and model quality for the above optimizers, run:
python -m kenning report \
--report-path build/yolact-report/report.md \
--report-name "YOLACT detection report" \
--root-dir build/yolact-report \
--img-dir build/yolact-report/imgs \
--report-types performance detection \
--measurements build/yolact-gpu-tvm.json build/yolact-gpu-onnx.json